

The X would be the number of atoms surrounding the central atom and E is the number of lone pairs around the central atom (A). The AX 3 VSEPR notation represents molecules that possess an ideal, planar symmetrical shape and molecular geometry. In a complete analysis of the geometry of a molecule it would be necessary to consider such factors as nuclear-nuclear interactions, nuclear-electron interactions, and electron-electron interactions. The A in the VSEPR notation means central atom. Despite this, the correct geometry is nearly always predicted, and the exceptions are often rather special cases. Assign an AX m E n designation then identify the LPLP, LPBP, or BPBP interactions and predict deviations from ideal bond angles. Determine the electron group arrangement around the central atom that minimizes repulsions. Organic molecules are treated just as successfully as inorganic molecules.Īpplication of the VSEPR method requires some simplifying assumptions about the nature of the bonding. This VESPR procedure is summarized as follows: Draw the Lewis electron structure of the molecule or polyatomic ion. It is a remarkably simple device that utilizes a simple set of electron accounting rules in order to predict the shape of, in particular, main group compounds. For main group compounds, the VSEPR method is such a predictive tool and unsurpassed as a handy predictive method. The bond angle is around 103 degrees (due to the repulsion of the lone pair). According to the above chart, we have a bent molecule structure. A central atom is defined in this theory as an atom which is bonded to two or more other atoms, while a terminal atom is bonded to only one other atom. The VSEPR notation for the OF2 molecule is AX2E2. The VSEPR notation for a phosgene molecule is AX3E0. VSEPR theory is used to predict the arrangement of electron pairs around central atoms in molecules, especially simple and symmetric molecules.
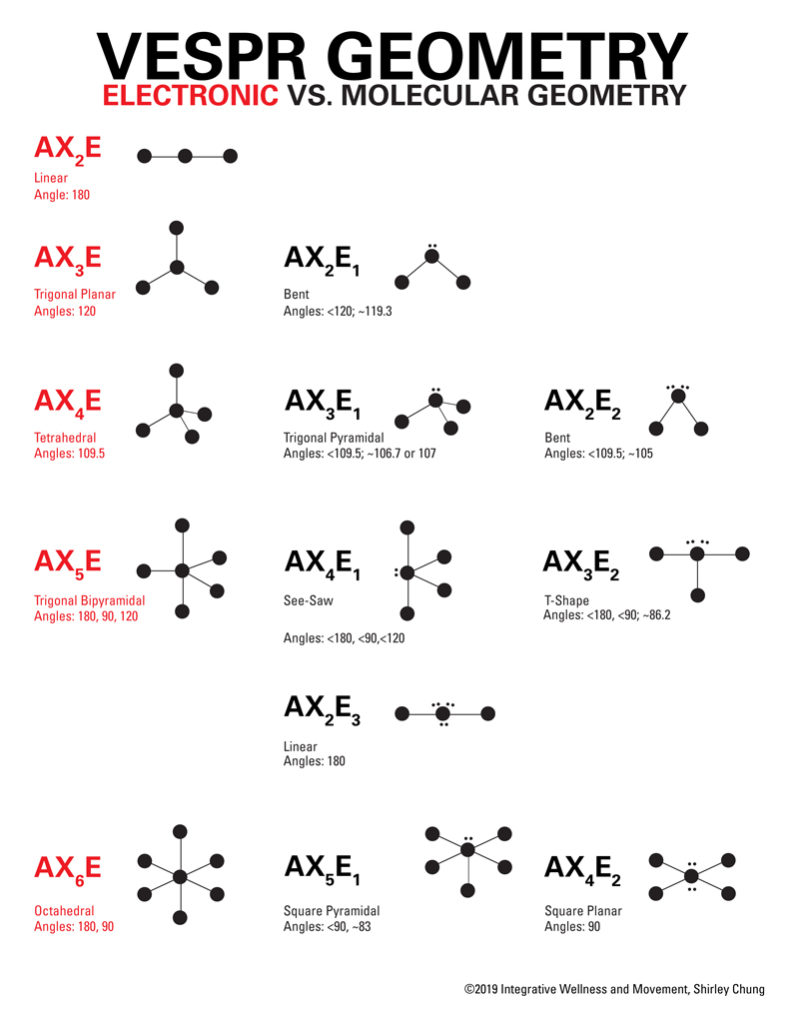
It is also desirable to have a simple method to predict the geometries of compounds. Specifically, VSEPR models look at the bonding and molecular geometry of organic. The valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) model focuses on the bonding and nonbonding electron pairs present in the outermost (valence) shell of an atom that connects with two or more other atoms.įundamentally, the VSEPR model theorizes that these regions of negative electric charge will repel each other, causing them (and the chemical bonds that they form) to stay as far apart as possible.It is very important to know the shape of a molecule if one is to understand its reactions. They move to be as far apart as possible while still maintaining the bonding. The valence-shell electron-pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory states that electron pairs repel each other whether or not they are in bond pairs or in lone pairs. VSEPR Theory: a chemistry model used to predict the shape of individual molecules based on electron-pair electrostatic repulsion The electrons around the atoms in a molecule repel each other.For example, carbon dioxide and sulfur dioxide are both species, but one is linear and the other is bent. Note, however, that not all species have the same molecular geometry. The main geometries without lone pair electrons are: linear, trigonal, tetrahedral, trigonal bipyramidal, and octahedral. This is 'VSEPR Notation, Bond Angles, Hybridization, Electron and Molecular Geometry' by Arielle Morris on Vimeo, the home for high quality. The valence shell electron pair repulsion theory or VSEPR theory is used to predict the three-dimensional shape of a molecule. The valence shell electron pair repulsion model is often abbreviated as VSEPR (pronounced 'vesper') and is a model to predict the geometry of molecules. VSEPR notation gives a general formula for classifying chemical species based on the number of electron pairs around a central atom.When lone pairs are present, the letter E x is added. 'A' represents the central atom and n represents the number of bonds with the central atom. The VSEPR notation for these molecules are AX n. Molecular geometries take into account the number of atoms and the number of lone pair electrons. VSEPR Notation As stated above, molecular geometry and electron-group geometry are the same when there are no lone pairs.Fundamentally, the VSEPR model theorizes that regions of negative electric charge will repel each other, causing them (and the chemical bonds that they form) to stay as far apart as possible.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
